Zero emissions in practice – reducing emissions in pharmaceutical chemistry
We incorporate zero emissions and energy consumption reduction into our everyday work in all cases. This time was no different. We started cooperation with a client from the pharmaceutical chemicals industry who was looking for opportunities to reduce the energy consumption of a group of plants throughout Europe. Based on the identified opportunities, we created a CO2 reduction map that meets the corporation's strategic assumptions. Effect? Identification of opportunities to reduce the energy consumption of a plant in Ireland by approximately 60% in a location where the client's team estimated this reduction at 7%.
First step
We started our cooperation with the client by formulating the most important problems and assumptions. The company's goal was to develop a CO2 reduction map aimed at making the plant zero-emission. The local energy efficiency team estimated the possible reductions in energy consumption at the Irish plant at around 7%. Thanks to the joint work of the team and DB Energy engineers, we managed to set a path for the client to modernize the plant's infrastructure, which then served as a map on the road to zero emission.
Realization of investments
At the client's plant, one of the problems was the implementation of modernization in various parts of the plant, which did not always go hand in hand with efficiency. Our experience shows that in many cases plants try to modernize their infrastructure but avoid optimization in production processes. Sometimes it happens that due to the lack of an appropriate strategy, they may reduce consumption in one place and eliminate this reduction in another.
At the client's facility in Ireland, we planned a detailed road map that indicated the optimal sequence of implementing activities in terms of reductions achieved, energy consumption, CO2 emissions and the costs necessary to incur:
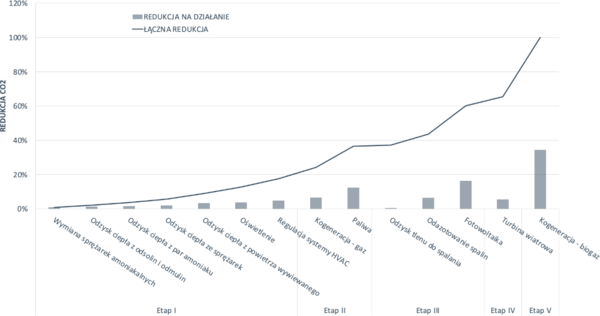
The path to climate neutrality implemented at our client from the pharmaceutical industry, developed on the basis of conducted audits.
After implementing the investment plan to reduce energy demand, we took further steps to electrify the plant and green energy sources. The key investment, from the energy and technological point of view, was the modernization of the waste incineration plant so that it could burn salty and non-saline waste simultaneously and the construction of a recovery boiler on this system.

Members of the DB Energy investment and automation department with the client's team at the new waste heat boiler.
The project was completed in March 2024.
Effects of modernization
- Total cost of modernization of the plant: PLN 16 million
- Total annual energy savings: approximately 12 GWh – approximately ¼ of the entire thermal energy consumption in the plant
- Payback period: approximately 5.5 years
- Reduction of carbon dioxide emissions: 2172 tCO2
- Additional investment budget that shortens the payback period to 2.5 years: AENA subsidy of approximately PLN 6 million
Thanks to just one modernization, annual CO2 emissions decreased by as much as 2,172 tons of carbon dioxide. The same amount of CO2 is emitted by driving around the world 400 times.
The above investment was important not only because of the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions but also because of the savings in natural gas consumption. Before the modernization, the Client used the main incinerator to burn non-saline waste and the second (reserve) one to burn salty waste. Thanks to the investment we have implemented, it will be possible to burn both types of waste in the main incineration plant. The second incinerator, on the other hand, will have an emergency function, used only during renovation shutdowns or maintenance works of the main incinerator, which will consequently lead to savings in natural gas consumption and related costs.
The corporation commissioning the investment is a large player in the pharmaceutical market. It has branches all over the world, and in Ireland alone, it employs over 1,100 people. The main area of activity of the facility is the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients).